
Author: Rishubh Madaboosi
Naperville Central High School
October 1, 2021
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this investigation was to determine if different genres of music had an effect on heart rate.
Procedure: Firstly, please go to a quiet room with all required materials, then record initial heart rate on google form using the heart rate monitor. After this, please connect headphones to the device and set volume to medium setting. Then please start to listen to the song given in the google form’s description, and at the halfway mark of the song, please record your heart rate on google form using the heart rate monitor. After finishing the song, please record the final heart rate in google form using the heart rate monitor.
Conclusion: After analyzing the data, the result was consistent with what the hypothesis assumed. When looking at the initial, ongoing, and final heart rates for classical music, 100% of the volunteers recorded a lower ongoing and final heart rate when compared to the initial heart rate. When looking at rock music, 60% of the volunteers recorded a lower ongoing and final heart rate when compared to the initial heart rate, while the other 40% recorded higher ongoing and final heart rates when compared to the initial heart rate.
Safety Sheet and Endorsements
All the volunteers in this experiment were asked to listen to music while recording their initial, ongoing, and final heart rates. Therefore, There are no safety concerns in this experiment.
Acknowledgements
I would like to acknowledge Mr. Golab for helping through the entire process of my research and for helping me understand how to do proper research at a higher standard. I would like to thank Dr. Rohit Loomba for helping to advise me and guide me through my research project. I would also like to thank all the people who helped during the testing stage of my experiment for volunteering and taking the time out of your day to help me in my research. I would like to thank my family for helping motivate me to push through with my work. I would also like to thank them for recommending me to take up this program.
Purpose
The purpose of this investigation was to determine if different genres of music had an effect on the heart rate of a human.
Hypothesis
If classical music was chosen to lower heart rate, it would be more successful in doing so when compared to rock music
Rationale: Classical music triggers certain emotions through different dopamine levels to order the brain to send messages through the nervous system to the sinus node telling it to either lower or increase the heart rate.
Review of Literature
Music is a big part of people’s lives and sometimes affects us in ways that we don’t always notice. With the growing popularity of listening to music while doing various activities like reading, exercising, etc, the question that comes to mind which music is best? The answer depends on the activity that is being accomplished. This is because different genres of music can have different effects on your body, like heart rate, blood pressure, and others. The purpose of
this investigation, then, is to determine if different genres of music have an effect on heart rate. This will be done in order to inform the people on how certain genres can be beneficial in certain circumstances.
According to an article from the National Library of Medicine, “How Does Music Affect the Human Body,” music is known to have certain effects on different parts and physiological variables of the body. To figure out how it could have an affect on a human’s heart rate, we need to examine how the body regulates the heart rate in different circumstances. According to royalsocietypublishing.org, the brain controls the heart rate directly through the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These two systems are a part of a bigger nervous system
called the autonomic nervous system. According to an article from byjus.com titled Difference Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic, the sympathetic nervous system is used to respond to perceived dangers, and the parasympathetic nervous system is used as a calming mechanism. These systems release different hormones that either accelerate or decelerate the heart rate. The sinus node is the pacemaker on the heart’s right atrium that releases electric impulses which start each beat of the heart. In an article from medicinenet.com, they say that the autonomic nervous system is said to directly control the sinus node which starts the cardiac cycle. The article goes on to say that the sinus node initiates the cycle by “generating electrical impulses and conducting them throughout the muscle of the heart, stimulating the heart to contract and pump blood.”.
It makes sense then, how the brain can send a message through the nervous system towards the sinus node to either speed up or slow down the heart rate. Music affects the heart rate of a human being because certain types of music trigger certain emotions in our body. According to dailygood.org, music can be used to peak emotions by increasing the amount of dopamine in your body. Dopamine is known as a feel good hormone, meaning that an increase in dopamine in a person’s body would make them feel very happy. Music acts as an independent variable by changing the amount of dopamine that flows through the body depending on the genre of music. Dopamine therefore can be used to change a person’s emotions depending on how much of it is used. A change in emotion can cause the brain to order different organs to act in a manner that best fits the setting that the human is in. To summarize this, music triggers a certain emotion through different dopamine levels and the brain sends messages through different nervous systems ordering the heart to change its pace.
The independent variable in this experiment are the genres of music because the genres are the variables being changed in order to get a different result from the heart rate. The dependent variable is the heart rate because the level of heart rate depends on what genre of music is being played.
In previous experimentation, an article titled, “Effects of music on systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate: a meta-analysis”, Dr. Rohit S. Loomba and Rohit Arora came to the conclusion that music has a beneficial effect in settings like emergency care units and other high anxiety environments, because it reduced heart rate, systolic, and diastolic blood pressure. This helps us understand that music does have an effect on our emotions, which in consequently has an effect on heart rate.
Other concepts that relate to the investigation could be, “What effect do different tones, tempos, and rhythms have on the entire body and the brain?” This question is similar to the different genres of music because different genres of music usually have different rhythms and beats that go along with them.
In conclusion, different genres of music cause different emotions to form based on the amount of dopamine that is produced as a result of listening to a certain genre. This then tells the brain to order certain actions from different organs to adjust to the new environment. One of these messages travel as neurons through the nervous system and go to the heart, where they order the sinus node to change the pace of the heartbeat. Based on this research, I can hypothesize that different genres of music will have an effect on heart rate and it will differ based on which genre of music is used.
Materials
- 1 heart rate monitor(or any device that can record heart rate)
- headphones
- device to play music
- A quiet room to do experiment
Procedure
- go to a quiet room with all required materials
- record initial heart rate on google form using the heart rate monitor
- connect headphones to device and set volume to medium setting
- listen to the song given in the google form’s description
- at halfway mark of the song, record heart rate on google form using the heart rate monitor
- after finishing the song, record final heart rate in google form using the heart rate monitor
Variables
- Independent variable: Genre of music (Rock or Classical)
- Controlled variables: gender, age, setting of location, volume, length of each song (within 30
seconds of each other) - Dependent variable: heart rates recorded
- Control: A comparison among the two genres of music
Results
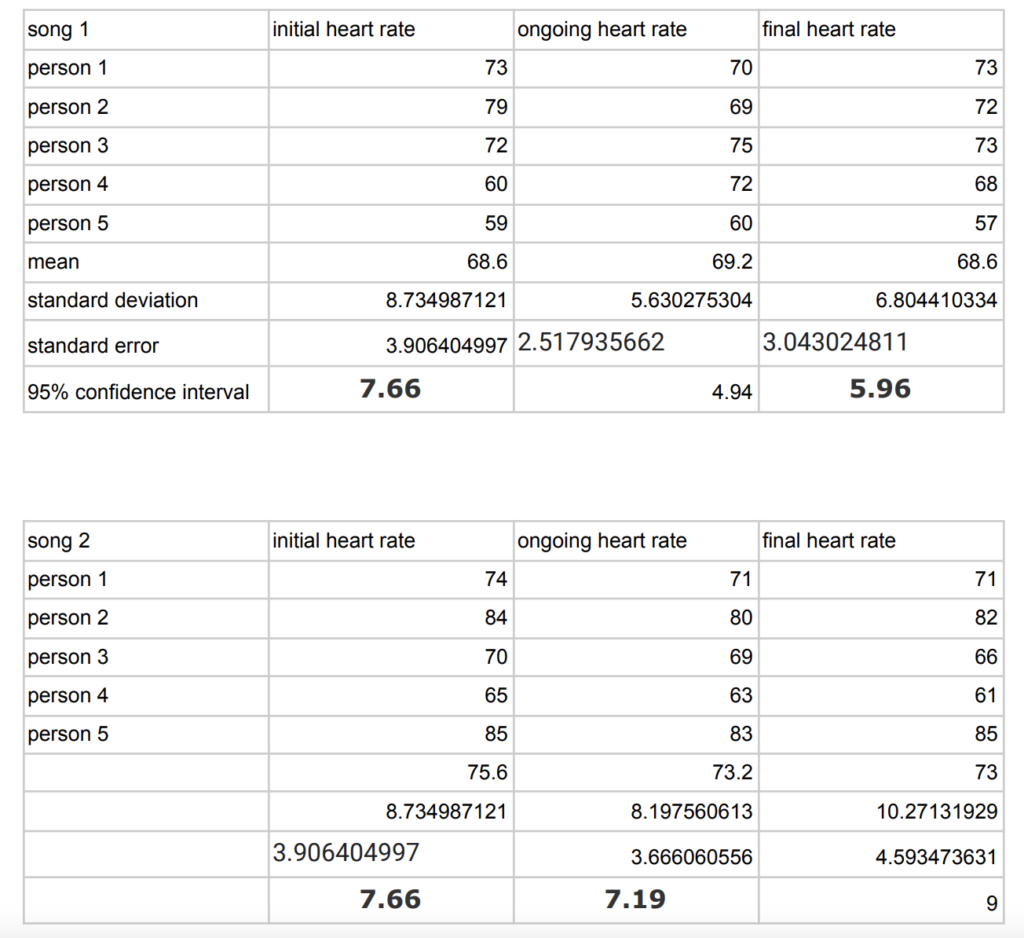
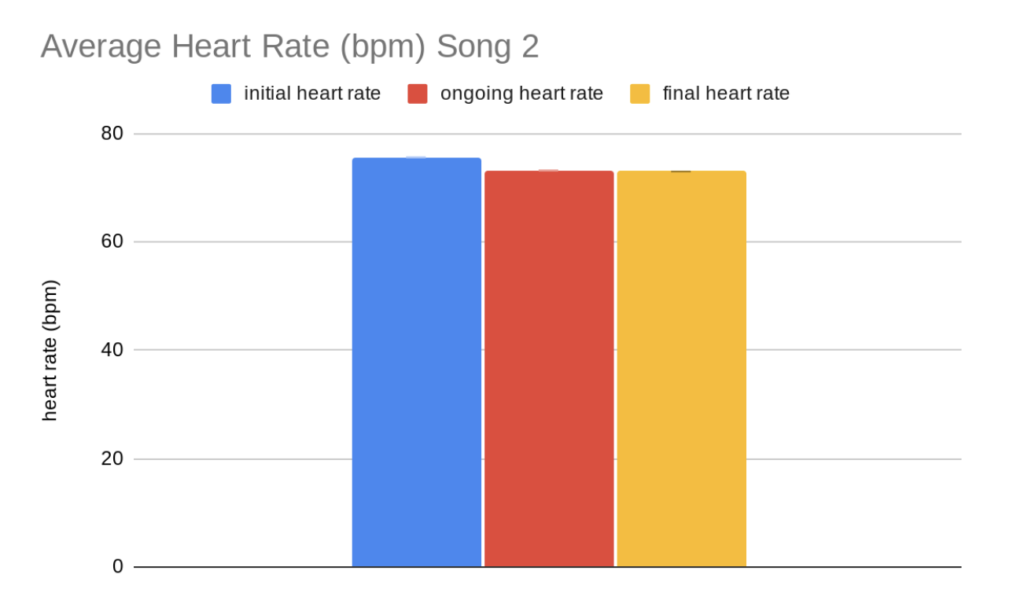
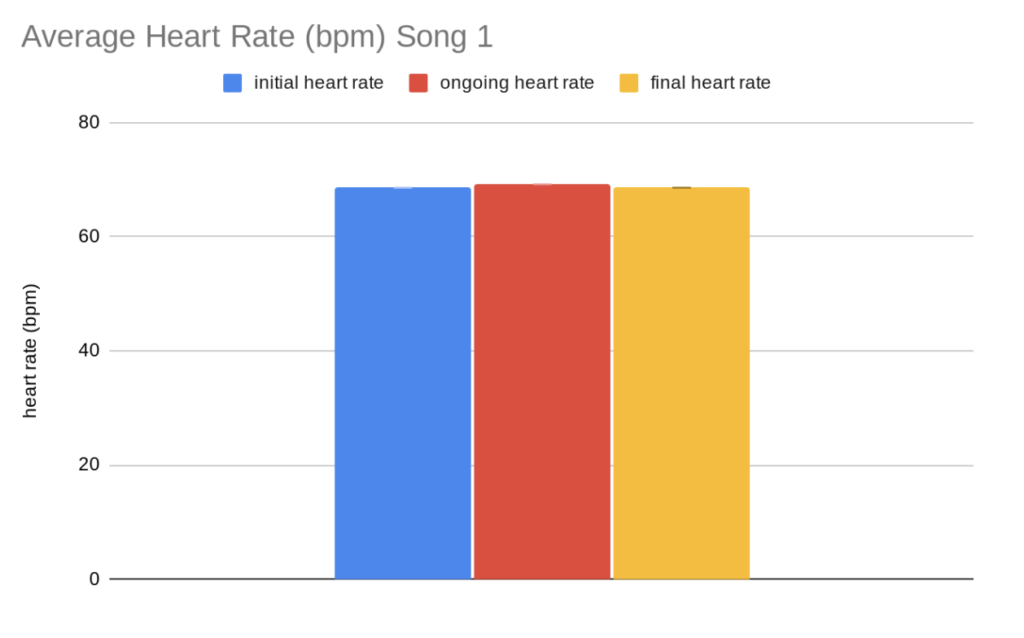
Data Analysis: The data shows the heart rates for each song from different genres. Song 1 is rock and song 2 is classical music. Along with the heart rates, the table also shows the average heart rate for each song, the standard deviation, standard error, and 95% confidence interval. The graph shows the average for each time when listening to the song (initial, ongoing, and final). The error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals.
Statistical analysis: In the graphs, the error bars are not overlapping which means that the data is significant, which shows that different genres of music have an effect on heart rate. In this experiment, there was evidence showing that classical music causes a decrease in heart rate 100% of the time, and rock music causes an increase in heart rate 60% of the time.
Error analysis: one of the main causes of error in the experiment could have been the preference of music. Because different people prefer different types of music to others, this can cause an increase in dopamine which can affect the heart rate of a person. For example, someone who enjoys rock music would most likely have a more evident heart rate change, whereas someone who does not enjoy it or has no opinion on it would have a less evident heart rate change or a heart rate change that is opposite to the trend.
Conclusion
To conclude my research, the data suggests that different genres of music do have an effect on heart rate. The data shows this idea because classical music is shown to lower the heart rate 100% of the time, while rock music is shown to increase the heart rate 60% of the time. The data is significant because the error bars between the two graphs do not overlap. Some things that could have been done to make the data more accurate is to find test subjects that do not have a preference for a certain genre of music, and do not have a disliking for a certain genre of music.
Reference List
Admin. (2021, January 14). Differences Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System. Retrieved January 31, 2021, from https://byjus.com/biology/difference-between-sympathetic-and-parasympathetic/#:~:text=Sympathetic%20Autonomic%20Nervous%20System%3A%20It,respiration %2C%20pupillary%20response%20and%20more.
Alessandro, S., Alessandro Silvani Alessandro Silvani http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3992-3892 PRISM Lab, Silvani, A., Alessandro Silvani http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3992-3892 PRISM Lab, Calandra-Buonaura, G., Giovanna Calandra-Buonaura Autonomic Unit, . . . Al., E. (2016, May 13). Brain–heart interactions: Physiology and clinical implications. Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsta.2015.0181#:~:text=10.1098%2Frsta.2015.0181-,Abstract ,central%20preganglionic%20and%20premotor%20neurons.
Bhandari, S. (2019, June 19). Dopamine: What It Is & What It Does. Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/what-is-dopamine#1
Change in Heartbeat. (n.d.). Retrieved January 11, 2021, from
https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/aa53422#:~:text=Your%20heart%20rate%20or%20rh
ythm,changes%20in%20your%20heart%20rhythm.
Emotions and Heart Health. (n.d.). Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=134&ContentID=165
Heart arrhythmia. (2020, August 09). Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-arrhythmia/symptoms-causes/syc-20350668
Loomba, R., Arora, R., Shah, P., Chandrasekar, S., & Molnar, J. (2012, May). Effects of music on systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate: A meta-analysis. Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3860955/ M;, M. (n.d.). [How does music affect the human body?]. Retrieved January 31, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10863350/#:~:text=Research%20has%20shown%20that%20mu
sic,influences%20immune%20and%20endocrine%20function.
Music & the Brain: The Fascinating Ways Music Affects Your Mood and Mind. (n.d.). Retrieved January 11, 2021, from http://www.dailygood.org/story/1613/music-and-the-brain-the-fascinating-ways-music-affects-yo
ur-mood-and-mind/#:~:text=Listening%20to%20music%20can%20create,brain’s%20reward%20
and%20pleasure%20centers.&text=The%20study%20incorporated%20specific%20songs%
20to%20portray%20different%20emotions.
Seladi-Schulman, J. (2018, July 23). What Part of the Brain Controls Emotions? Retrieved January 6, 2021, from
https://www.healthline.com/health/what-part-of-the-brain-controls emotions#:~:text=The%20limbic%20system%20is%20a,for%20behavioral%20and%20emotional%20responses
UC Davis Health, S. (n.d.). Heart Rate. Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://health.ucdavis.edu/sportsmedicine/resources/heart_rate_description.html#:~:text=The%20 sympathetic%20nervous%20system%20(SNS)%20releases%20the%20hormones%20(catechola mines,to%20slow%20the%20heart%20rate.
William C. Shiel Jr., M. (2018, December 27). Definition of Sinus node. Retrieved January 11, 2021, from https://www.medicinenet.com/sinus_node/definition.htm
About the author

Rishubh Madaboosi
Rishubh is a Senior at Naperville Central High school in Naperville, Illinois. He has a passion for behavioral science and different fields involving biology. Besides his academic interests in biology and history, he enjoys playing tennis for the school team and playing clarinet in his free time.
